Commonwealth Fraud and Corruption Control Framework 2024
Table of contents
The Commonwealth Fraud and Corruption Control Framework supports Australian Government entities to effectively manage the risks of fraud and corruption. The framework comes into effect on 1 July 2024.
The framework consists of 3 parts:
- Fraud and Corruption Rule (Section 10 of the PGPA Rule 2014)
- Fraud and Corruption Policy
- Fraud and Corruption Guidance (Resource Management Guidance 201 – Preventing, detecting and dealing with fraud and corruption).
Fraud and Corruption Rule
This is a legislative instrument for all PGPA Act entities from 1 July 2024. It sets out the minimum standards for accountable authorities of PGPA Act entities for managing the risk and incidents of fraud and corruption relating to their entity. The Rule requires accountable authorities to take all reasonable measures to prevent, detect and respond to fraud and corruption relating to the entity.
Fraud and Corruption Policy
This policy is for all Non-Corporate Commonwealth Entities (NCEs) from 1 July 2024. Corporate Commonwealth Entities (CCEs) and Commonwealth Companies are encouraged to adopt the Fraud and Corruption Policy as best practice. The Fraud and Corruption Policy sets out the procedural requirements entities must implement to establish and maintain an appropriate system of fraud and corruption control for their entity.
Fraud and Corruption Guidance
This provides further guidance on fraud and corruption control arrangements for all Commonwealth entities.
The framework’s key elements
The below diagram shows how the 8 different Policy Elements work to support a coordinated system of accountability for protecting public resources from fraud and corruption across the Commonwealth.
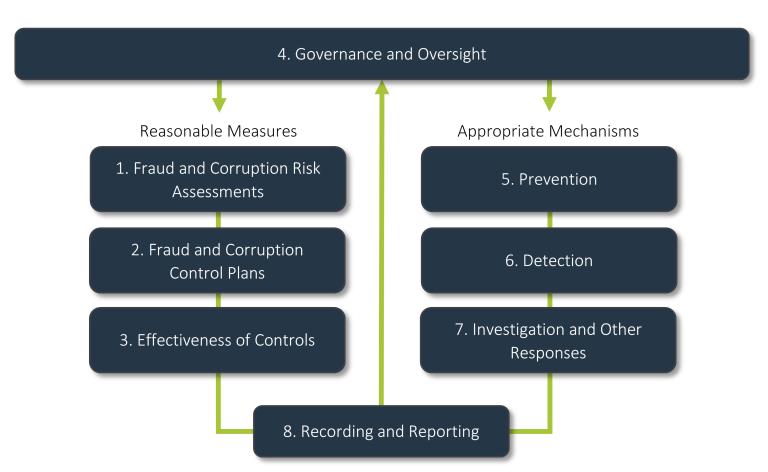
Fraud and corruption risk assessments help entities identify, understand and document their exposure to fraud and corruption, the associated risks and their existing control arrangements.
Fraud and corruption control plans help entities document, communicate, manage and monitor the current or planned activities to manage the entity’s identified fraud and corruption risks.
Periodically reviewing the effectiveness of controls helps entities ensure their most important controls are working to mitigate the entity’s identified fraud and corruption risks.
Appropriate governance and oversight structures that are proportionate to the operating environment of an entity and integrated with an entity’s risk management framework are essential for effective fraud and corruption management.
Prevention is efficient and cost-effective for minimising the risk of fraud and corruption and can eliminate or reduce the harmful consequences to Commonwealth entities and third parties, including significant financial and reputational harm.
Detection of fraud and corruption can involve a range of mechanisms including: reporting channels for officials, third-party service providers and members of the public, automated transaction monitoring, account reconciliation, management reviews and audits, and data matching and analytics.
Effective responses to fraud or corruption incidents can involve a range of administrative, civil and criminal interventions, including containment, disruption, investigation, referrals to the Australian Federal Police or National Anti-Corruption Commission (or the Inspector General of Intelligence and Security for intelligence agencies), disciplinary action, recovery, remediation and where appropriate, prosecution.
Recording and reporting incidents of fraud or corruption, suspected fraud, corruption requires effective information management systems to capture allegations and instances of fraud and corruption, or attempted fraud and corruption, and the subsequent response and outcomes. Reporting should provide data about the nature, extent and location of fraud and corruption against the entity. A feedback loop of internal reporting supports an entity to maintain oversight over mechanisms for preventing, detecting and responding to fraud and corruption, and remain compliant with the Fraud and Corruption Rule and Policy.

